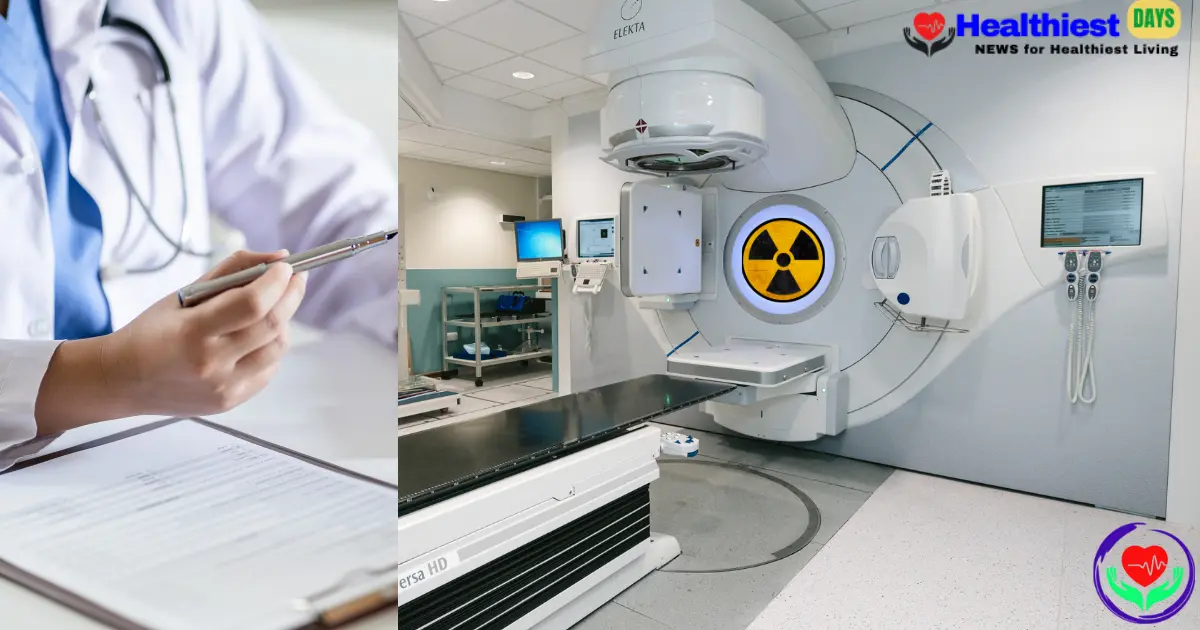
Understanding the Role of Radiation Treatment for Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is very often referred to as the “silent killer” due to its ambiguous, uncertain symptoms and late-stage detection. It is noted that it is almost the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women in the United States, with more than 19,000 women expected to be diagnosed this year. Radiation treatment strategies for ovarian cancer vary depending on the cancer stage, location, and overall health of the patient.
While surgery and chemotherapy are commonly used, radiation treatment for ovarian cancer plays a supportive but sometimes crucial role in managing the disease, particularly when it recurs or spreads. In this blog post, we will investigate how radiation therapy fits into the ovarian cancer treatment landscape, which types exist, and how to prepare before and recover from this treatment.
What Is Radiation Therapy/Treatment?
As a matter of fact, radiation therapy is a localized cancer treatment that basically uses high-energy X-rays or particles to target and destroy cancer cells. In this technique the rays damage the DNA of cancerous cells, which prevents them from growing or dividing.
Contrary to chemotherapy, which works throughout the entire body, radiation is designed in such a way that it focuses on a specific area, making it highly effective in targeting localized tumors or metastases.
Cancer care involves two main basic types:
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT)
- Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy)
Each one of the types has its own role, especially when the question of treating gynecological cancers like ovarian cancer comes to mind.
Is Radiation Commonly Used for Ovarian Cancer?
You should be aware of the fact that radiation therapy is not typically the first line of treatment for ovarian cancer. That role is generally reserved for:
- Surgery—to remove the tumor or ovaries
- Chemotherapy—to attack cancer cells systemically
However, the role of radiation becomes valuable and impactful in specific circumstances, like
- When the cancer returns in a localized area
- When surgery is not an option
- To control symptoms (like pain or bleeding) in advanced stages
- When metastases are limited and need targeted treatment
In situations like these above, radiation may significantly improve the patient’s quality of life and help prolong survival.
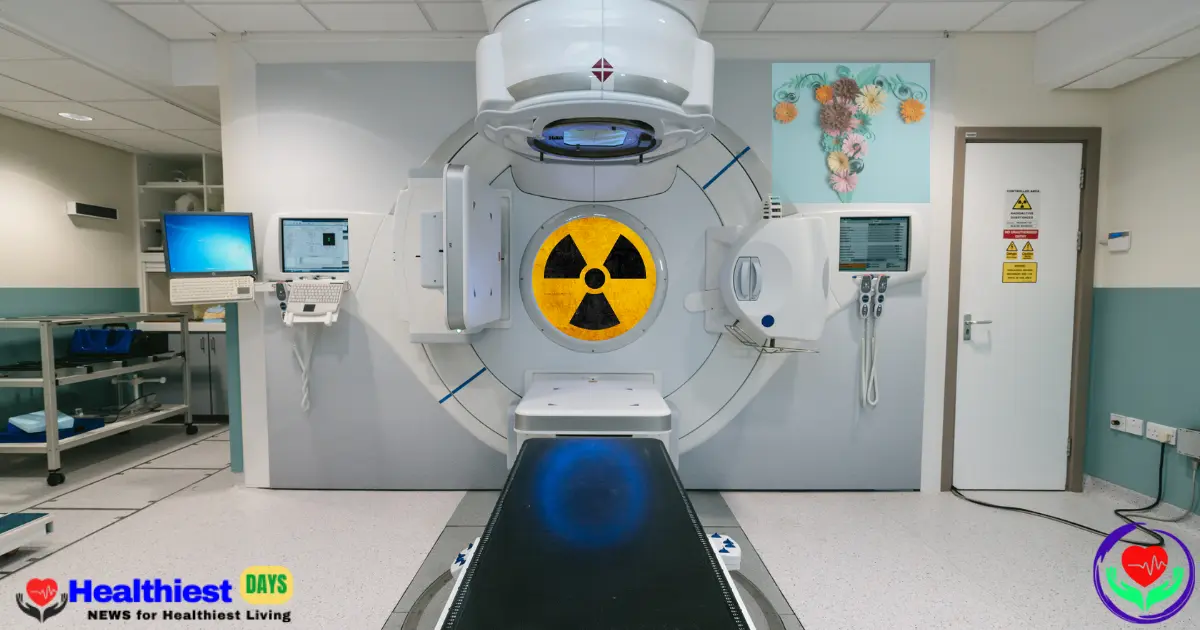
Types of Radiation Treatment for Ovarian Cancer
1. External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
Talking about EBRT, this is the most common form of radiation used in ovarian cancer. In EBRT, a machine outside the body is used to deliver radiation precisely to the affected area with accuracy, such as the pelvis or abdomen.
- Schedule: Its schedule involves 5 days a week for 2 to 6 weeks
- Non-invasive and is performed in an outpatient setting
- It is ideal for recurrence in the pelvis or abdominal cavity
2. Brachytherapy (Internal Radiation)
Interestingly, brachytherapy involves placing a radioactive source directly inside the body, near the tumor. But this method is less common in ovarian cancer yet can be used in rare, localized, and special cases. It triggers a high dose of radiation with minimal exposure to surrounding tissues.
3. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
In SBRT, highly focused and intense doses of radiation are delivered to small, specific areas; it is often used in recurrent or metastatic cases. It is worth noticing that it is considered when the cancer has spread to limited sites such as lymph nodes, bones, or liver.
What to Expect During Radiation Treatment
You should be aware of the fact that radiation treatment for ovarian cancer may sound intimidating, but it is typically quick and painless.
Steps Before Treatment:
- You will undergo a simulation scan to map your treatment area
- A customized radiation plan is designed using CT or MRI images
During Each Session:
- Sessions last 15–30 minutes of duration
- You will lie still while a machine triggers radiation to the targeted site
- In this procedure, no cuts, needles, or pain are involved.
Duration of Treatment:
- It usually spans over a few weeks; that depending on your plan
Your radiation oncologist and care team will explain each step to ensure that you are comfortable and well informed.
Potential Side Effects of Radiation Therapy
In fact, radiation is generally well-tolerated, yet some side effects may occur, especially when the pelvis or abdomen is targeted.
Short-term side effects may include:
- Fatigue (which is most common)
- Nausea or changes in appetite
- Skin irritation occur at the treatment site
- Mild bowel issues (i.e., diarrhea, cramping)
- Bladder discomfort
Long-term side effects may involve:
- Bowel or bladder complications (rare cases)
- Fertility issues
- Nerve damage (rare in pelvic radiation)
Your professional doctor may adjust your plan or recommend medications when needed to manage these symptoms. Most of the effects fade out gradually after treatment ends.
Recovery and Life After Radiation Therapy
Factually speaking, it is also noted that radiation recovery is often faster as compared to chemotherapy, but your body still needs time to heal naturally.
Post-treatment tips include:
- Take plenty of rest and hydration
- Eat a diet which will be nutrient-rich and anti-inflammatory
- Track side effects and instantly report them to your doctor
- Join support groups for emotional resilience
It is professionally experienced that many women resume normal activities within weeks, but your energy levels may take time to bounce back, so be careful.
At the Healthiest Days, we emphasize holistic healing backed by nature—supported by medical care with wellness practices to support full recovery of you.
Combining Radiation with Other Treatments
It’s worth noticing that radiation rarely acts alone in ovarian cancer management.
Radiation and Chemotherapy or Surgery:
- Keep in mind that radiation may follow chemotherapy or surgery to target remaining cancer cells
- In recurrent or chronic cancer, it may be used in combination with systemic therapies
Palliative Radiation:
In advanced stages, radiation is very beneficial and highly effective at relieving pain, stopping bleeding, or relieving organ pressure, which improves comfort and dignity in late-stage care.
Questions to Ask Your Oncologist/Therapist
In order to make a decision for the treatment, knowledge is power especially prior to a cure. So, ask your doctor questions like
- Is radiation therapy suitable for my type, age and stage?
- What are the possible expected outcomes and side effects?
- Will it affect my fertility or hormones?
- Can radiation be combined with other therapies?
- How will it impact my quality of life?
There is a dire need to inquire about those questions, which helps ensure that your care is both personalized and effective and that you are much more conscious.
Final Thoughts: Is Radiation Treatment for Ovarian Cancer Right for You?
The crux of the discussion is that radiation therapy may not be the most common approach for ovarian cancer, but in specific cases it plays a vital role—especially for recurrence, symptom control, and precision targeting of small metastases. It is basically a unique way used to enhance quality of life and extend survival chances when other options are limited.
The key to successful treatment is a customized treatment plan built by a multidisciplinary team of professionals. If it is suggested by your doctor to adopt for radiation treatment option, then be sure to know that it is backed by research, experience, and evolving technologies that are designed to target cancer while preserving healthy tissue.
FAQs
1. Is radiation treatment for ovarian cancer painful?
No, radiation therapy is not a painful procedure. Some people may experience mild side effects like fatigue or nausea afterward, which are common.
2. How long does radiation treatment for ovarian cancer take?
Most of the courses last between 2 and 6 weeks, with sessions scheduled five days a week according to the severity of the cases.
3. Can radiation therapy cure ovarian cancer?
Factually, radiation is usually not curative on its own, but it can control or reduce cancer parts, especially in recurrence or localized areas.
4. At which stage of ovarian cancer is radiation used?
Radiation is mostly used in recurrent or advanced stages, or for palliation, and not typically used in early stages of treatment.
5. What is the success rate of radiation therapy for ovarian cancer?
Success rate varies based on the cancer’s stage and spread. It is often effective in slowing tumor growth and relieving symptoms in advanced or recurrent cases.
Call to Action
At HealthiestDays, we believe in empowering your healing journey naturally and intentionally. Whether you want to know treatment options or are recovering from ovarian cancer, our expert-backed wellness guide, recovery plans, and supportive resources are here to help you out.
👉 Visit healthiestdays.com and discover a better way to heal—because you deserve care without compromise.