Introduction:
If you are experiencing symptoms like bad breath, swollen gums, bleeding in teeth, or in case you are losing teeth, there is a high probability that you have periodontal disease. This happens when there is an infection or inflammation in your gums or the bone that supports your teeth.
Now you must be asking yourself questions like how it can be treated, is periodontal disease communicable, how I even got it in the first place, what could be done to prevent it, etc. In this blog, we will answer your questions about periodontal disease.
What Is The Difference Between Periodontal Diseases: Gingivitis and Periodontitis?
Periodontal disease has different stages, and if the mildest diseases are left untreated for a long time, then they turn into very serious dental issues.
Gingivitis is a periodontal disease, but it is a mild form of this disease. It happens when there is plaque buildup on the teeth and below the gum line. It is usually not super painful, but it must be treated effectively; otherwise, it can turn into a bigger problem, i.e., periodontitis.
What happens in Periodontitis is that the bacteria that’s present in the plaque starts to irritate the gums, making them inflamed. The connective tissues that basically hold our teeth in the sockets are eaten up by this infection. In such a case, it becomes somewhat painful to properly clean your teeth, which means more plaque keeps building up, which leads to more inflammation, more pain, and eventually bone loss around the teeth.
Thus, it is crucial to get gum disease treated in the very early stages before it turns into long-term complications.
Symptoms Indicating You Have A Gum Disease:
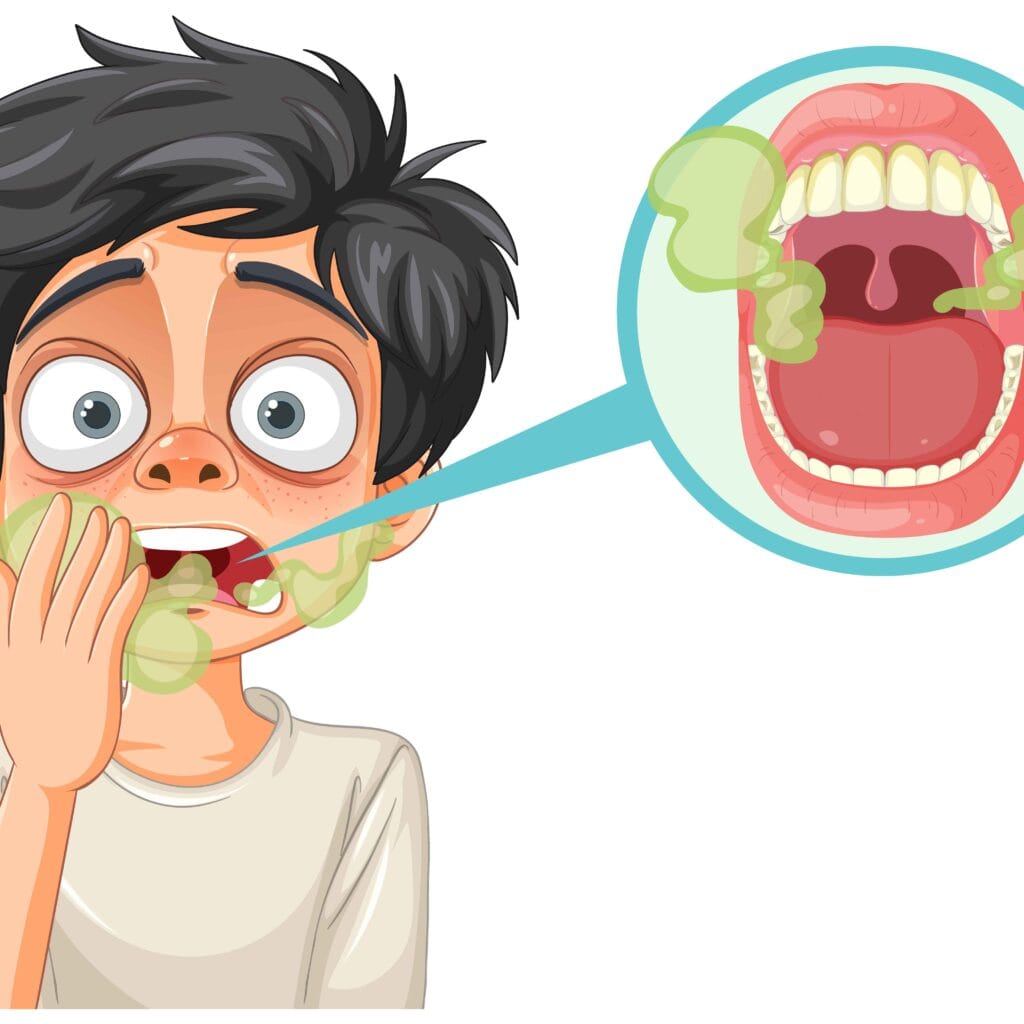
If you have gingivitis or periodontitis, you might be wondering how you even ended up in such a situation. The thing is, we often ignore the early symptoms until it’s too late. You keep thinking this is just a random toothache that will go away, but then your gums start bleeding. You do some home remedies, thinking it’s not that serious, and at last, here you are with a huge oral condition now. It is essential to recognize the symptoms so that you can address them promptly. Common symptoms are:
| Symptoms | Detail |
| Bad Breath | Consistently having bad breath is called halitosis, and it is usually a result of plaque formation and the accumulation of bacteria in the mouth |
| Swollen Gums | Due to inflammation, the gums become red and swollen, which makes the gums look puffy and tender to the touch sometimes |
| Bleeding Gums | If your gums bleed every time you brush or floss, it is a sign of an underlying gum disease |
| Receding Gums | Gums start to pull away from the teeth, exposing their roots and giving teeth an elongated look |
| Loose Teeth | In case of advanced periodontal diseases, tooth stability is compromised, resulting in teeth loosening or even shifting |
| Formation Of Pockets | There can be spaces between gums and teeth where bacteria start collecting |
| Changes In Bite | Misalignment of how teeth fit together when biting means this shift has occurred due to periodontal disease |
| Painful Chewing | Because of the damage to the supporting structure of the teeth and because of inflammation, it becomes uncomfortable to chew |
| Pus Between Teeth And Gums | The presence of pus confirms that the infection is getting advanced, and it requires urgent and proper dental intervention |
Answering the Biggest Concern: Is Gum Disease Contagious?
The answer to the question “Can gingivitis spread?” is yes, but there needs to be a deeper understanding of why it is so. First of all, we need to better understand the concept of contagiousness itself. The ability of a condition or a disease to be transmitted from one person to another is called contagiousness. When it comes to gum disease, we need to understand that the infection itself and the risk factors that come with this disease are two different things. Because the infection itself is not what is contagious, it is some habits and behaviors that transmit it from one person to another.
How Gum Disease Is Transmitted:
This is the important question to ponder upon here. Gum diseases are not spread like the flu or common cold through casual contact or through airborne particles. The bacteria that causes gum disease is transmissible through saliva and oral fluids. So activities like sharing utensils, kissing, using the same toothbrush, sneezing, coughing, sharing food, etc., are some things that result in periodontal bacteria transmission, thus increasing the chances of transmitting gum diseases from one person to another.
People Most At Risk of Developing Gum Disease:

One important thing to note here is that gum disease is not always a result of harmful bacteria. Yes, those who are more exposed to harmful bacteria are at risk, but there are other risk factors in play as well. The National Institute of Dental Health and Craniofacial Research reports several causes of gum disease. People who have these habits are at higher risk of getting gum disease.
- Smoking or using tobacco
- Having chronic illnesses like diabetes
- Not maintaining proper oral hygiene
- Hormonal changes or pregnancy
- Family history of gum disease
- Constantly living in a state of stress
- Having autoimmune diseases like Scleroderma, Lupus, Crohn’s disease, etc.
All of the above are risk factors when it comes to gum disease. It is important to know all these contributors to gum disease so that you can opt for the right strategies of prevention.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease:
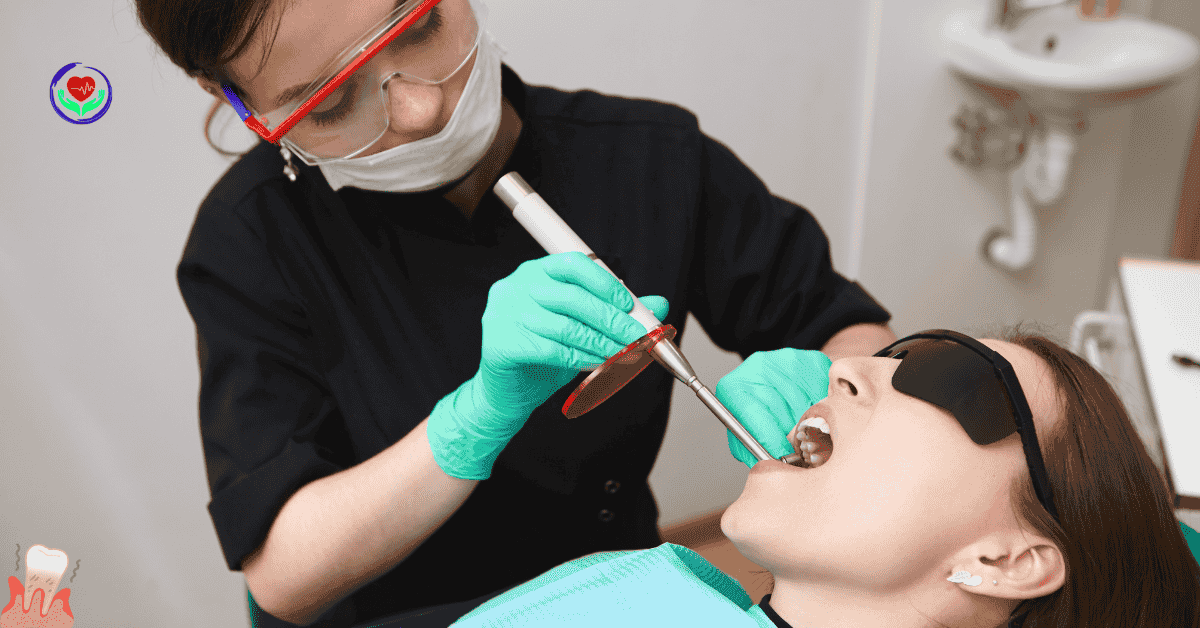
Professional dentists will check your gums and teeth and suggest a periodontal treatment that is appropriate to your needs and stage of the disease. Some common effective periodontitis treatments include:
- Antibiotics: antibiotics can be prescribed to control bacterial infection, and they also help in healing
- Scaling and Root Planning: this is a deep cleaning process in which plaque and tartar are removed from below the gumline, smoothing the roots of the teeth to promote healing
- Laser Therapy: this is an advanced process that promotes regenerating gum tissues by targeting and removing infected tissue with laser technology
A periodontist in Houston who has been practicing for 25 years reports a case of a patient who was 32 years old and was experiencing severe gum disease symptoms, including gum recessions, deep pockets, tooth mobility, etc. But the patient’s oral health was restored with treatments like root planning, scaling, and surgical interventions, even though his symptoms were severe. This shows that early intervention can always halt a serious and advanced case of periodontitis.
Preventing Periodontal Infection:
The CDC offers prevention tips for gum disease.
- Brush your teeth twice every day
- Make flossing a regular habit
- Discuss with your dentist and start using an antimicrobial mouthwash on their recommendation
- Be cautious and avoid sharing saliva with someone who has poor oral hygiene, i.e., don’t share food, cups, toothbrushes with, or kiss someone with oral health issues
- Pay regular visits to the dentist for tooth and gum checkups, including getting your teeth cleaned by a dentist every 6 months
- Make sure you consume a healthy diet because it is the key to having a strong immune system and better health overall
Are You Experiencing Gum Disease Symptoms?
If you are suffering from any of the symptoms of gingivitis or periodontitis, it is time to see your dentist right away. Not only is this condition going to affect your health, but since it can be transmitted to other people, you are putting them at risk, too.
Conclusion:
People who have poor oral hygiene, chronic illnesses, or who smoke, or are going through hormonal changes, are very prone to developing periodontal disease. Periodontal disease is communicable, but its transmission can be lowered by following the right protocol. There are effective treatment options available, and with proper care, you can prevent getting gum disease.
FAQs:
Q: Are gum diseases easily transmitted?
Gum diseases are not directly transmissible, and they do not spread through contact or air; they spread because of different behaviors, like sharing utensils or a toothbrush with someone who has oral health problems.
Q: I brush my teeth every day, but still have gum disease symptoms. How is it possible?
There can be many causes of gum disease other than plaque formation from not brushing your teeth, like genetics, hormonal changes, smoking, chronic illness, etc.
Q3: Which treatment is the best for gingivitis and periodontitis?
The treatment that will be most suited for you depends on the severity of your problem. Consult a dentist and get your gums and teeth checked to know where you stand and what the dentist recommends to be your best option for treatment.